A CASE OF 42 YEAR OLD FEMALE WITH MULTIPLE HEALTH EVENTS SINCE BIRTH
I have been given this case to solve in an attempt to understand the topic of "patient clinical data analysis"to develop my competency in reading and comprehending clinical data icluding history,clinical findings,investigations and come up with a diagnosis and treatment plan.
You can find the entire real patient clinical problem in this link below.....(https://classworkdecjan.blogspot.com/2019/05/42-f-with-severe-regular-edema-with_17.html?m=1)
Following is my analysis of the patient's problem:
The problems in order of priority are:
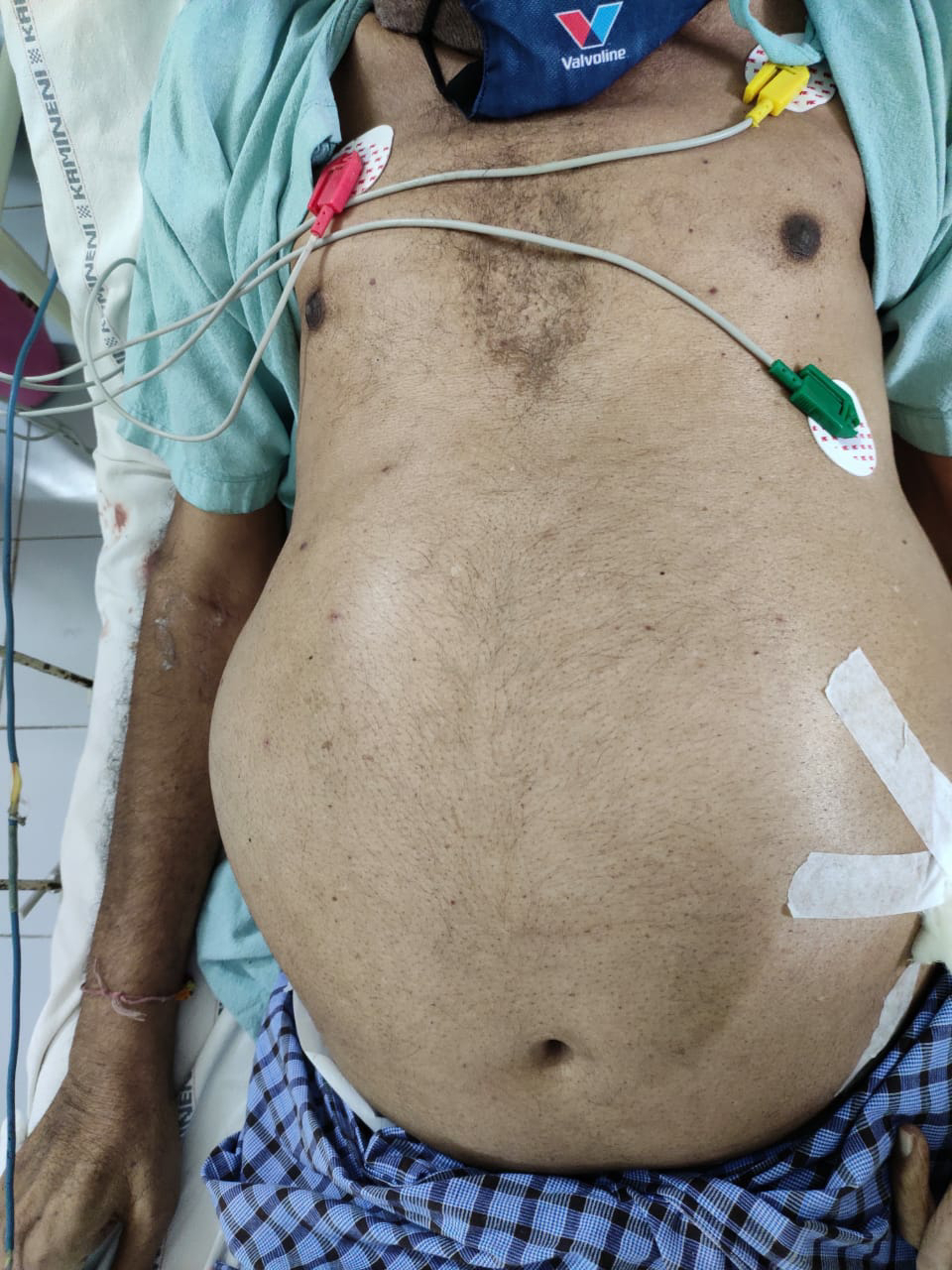
- SWELLING
- HEADACHES
- LEFT-SIDED WEAKNESS
- SLEEP DEPRIVATION
- EXERCISE INDUCED FATIGUE
Reasons for the above problems:
1.SWELLING
It started at the age of 1 and patient still swells up in conditions of:Emotional stress,exercise,smoking or eating the wrong thing.Swelling is mainly in face,neck region and abdomen.
It might be a part of hemolytic crises occuring in patient due to G6PD deficiency.
G6PD DEFICIENCY
It is a X-linked intermediate disease.HMP shunt pathway is affected in this condition where there is decreased production of NADPH.NADPH maintains the levels of reduced glutathione which inturn maintains the RBC integrity.
If the reduced glutathione levels are low then the RBCs become fragile and when they are subjected to oxidative stress undergo hemolysis.
POSSIBLE TRIGGERS IN THIS PATIENT ARE:
- Infections:recurrent UTI and pneumonia infections
- Severe reaction to antimalarials
- Severe reaction to sulfa drugs
- Severe edema after FAVA BEANS ingestion
Following these triggers the patient had symptoms suggestive of hemolysis like coke coloured urine(hemoglobinuria),diarrhoea,vomiting,swelling and acute kidney injury.
FURTHER EXAMINATION AND INVESTIGATIONS
- Any episodes of jaundice?
- Any other specific triggers for hemolysis?
- Complete blood picture,Retic count
- Liver enzymes
- Raised Lactate dehydrogenase levels (sign of intravascular hemolysis)?
- Decreased Haptoglobin levels?
- Raised unconjugated bilirubin levels?
- COOMBS TEST which is negative as G6PD deficiency is non immune mediated hemolytic anemia.
- SPECIFIC TEST:BEUTLER FLOURESCENT SPOT TEST.
- Peripheral smear examination:Bite cells,Blister cells,HEINZ bodies.
SUGGESTED TREATMENT
- Avoiding oxidative stress.
- Vaccination against pneumonia is taken ehich helped in preventing infection induced attacks of hemolysis to some extent.
- In acute phases, blood transfusion may be necessary.
- Apple has good antioxidant properties which the patient is taking daily.
2.HEADACHES
Severe headaches started at the age of 2 and became worse with menses at age 14.
Attacks increased in severity over time.
They are preceded by aura mainly visual.
MIGRAINE
Migraine headache is episodic and 20% are classical (associated with aura).
DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA FOR MIGRAINE:
Repeated attacks of headache lasting for 4-72 hours in patients with normal physical examination and no other reasonable cause for headache and atleast 2 of the following:
- Unilateral headcahe.
- Throbbing pain.
- Aggravated by movement.
- Moderate to severe intensity.
plus atleast 1 of the following:
- Associated nausea and vomiting.
- Photophobia and phonophobia.
CHARACTERISTICS OF AURA:atleast 3 of the following:
- Gradual onset.
- Lasting <60 minutes.
- Fully reversible.
- Followed by headache within 60 miuntes or headache simultaneously with aura.
- Not attributable to other disease.
FURTHER INVESTIGATIONS
- Fundus examination: look for papilloedema: sign of raised ICT and helps in ruling out Dangerous type of headache.
- CT and MRI
- XRAY paranasal sinuses
SUGGESTED TREATMENT
ACUTE MODERATE TO SEVERE ATTACK;
Triptans (5HT 1B/1D agonists) are used.
Newer modality of treatment:ERENUMAB:monoclonal antibody against CGRP(calcitonin gene regulated peptide).
3.LEFT SIDED WEAKNESS
Numbness in left side of face, loss of function on left side of the body.
Had this type of weakness at the time of migraine attack.
Passible dignosis could be HEMIPLEGIC MIGRAINE.
4.SLEEP DEPRIVATION
Low REM sleep
Less duration : 2-4 hours
Causes for sleep problems:low NADPH ,low glycine and AMPD1 deficiency( increased adenosine levels).
SUGGESTED TREATMENT
L-Serine acts similar to glycine and improves the quality of sleep.
5.EXERCISE INDUCED FATIGUE
ADENOSINE MONOPHOSPHATE DEAMINASE 1 DEFICIENCY
Excess adenosine causes decreased alertness and fatigue.
Exercise intolerance,muscle pain,muscle cramping are seen.
SUGGESTED TREATMENT
Ribose (0.2 g/kg) daily and hourly dosing provides direct source of energy for cells in cases of exertion.
OTHER PROBLEMS OF THE PATIENT
- MTHFR (Methylene tetrahydrofolate reductase) MUTATION
Increased homocysteine levels,decreased folate and B12 levels.
Associated with:Digestive issues,migraines,depression, anxiety,bipolar disease,peripheral neuropathy and scoliosis.
TREATMENT:Folate,Vitamin B6,12 supplements,methionine and 5-MTHF.
- WNK1 MUTATION
It is a serine threonine kinase which helps in regulation of cation-chloride cotransporters.
Associated with familial hyperkalemic hypertension syndrome.
- HAIR LOSS
- DEGENERATIVE SPINE,HIP AND KNEE PROBLEMS
For which i couldn't find definite reasons.

Comments
Post a Comment